Substitution Mutation
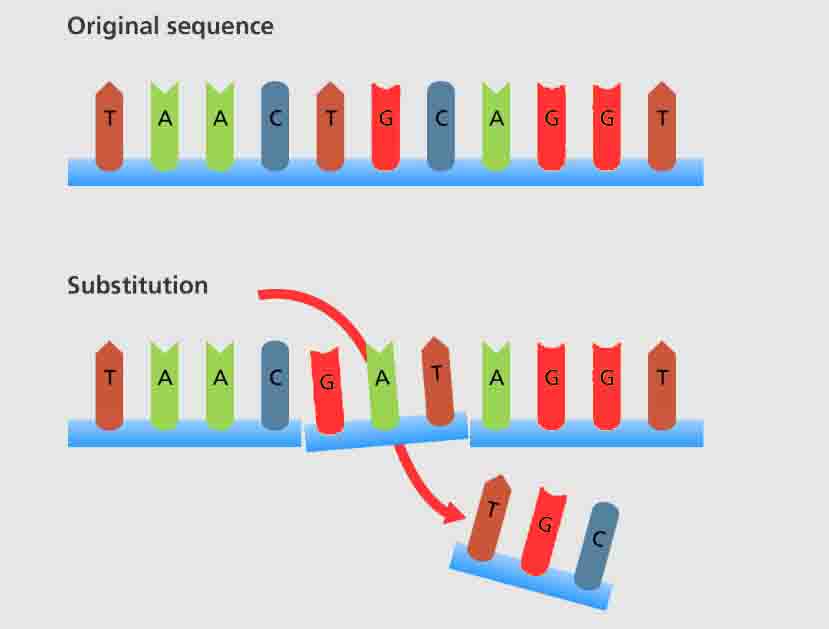
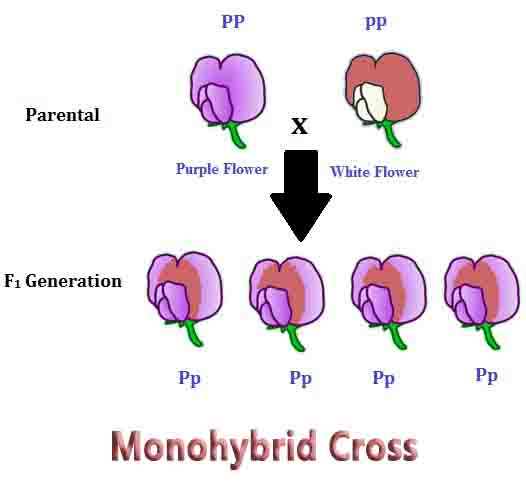
Substitution Mutation Definition A substitution mutation is a type of replication error during DNA replication which places the wrong nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides in the wrong position. A type of substitution mutation, a point mutation, occurs which a single nucleotide is substituted. Importantly, a substitution mutation results in DNA of the same length. It … Read more